The Definitive Guide to Healing a Torn Labrum in the Hip
Key Takeaways:
- The labrum is a piece of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the hip joint and provides stability and cushioning.
- A torn labrum in the hip can result from traumatic injuries, repetitive motions, structural abnormalities, or degenerative changes.
- Physical indications of a torn labrum include hip joint instability, limited range of motion, clicking or locking sensation, and pain with specific movements.
- Typical symptoms of a torn labrum include pain in the hip or groin area, difficulty walking or running, stiffness, and clicking or popping sensations.
- Diagnosis may involve physical examination, MRI, X-rays, or hip arthroscopy.
- Non-surgical treatment options include rest, physical therapy, medications, and injection therapy.
- If conservative measures fail, surgical intervention such as hip arthroscopy may be necessary.
- Recovery and rehabilitation can take several months and involve different phases focusing on reducing pain, regaining range of motion, strengthening, and gradually returning to functional activities.
- Exercises and stretches to aid in healing include hip strengthening exercises, range of motion exercises, core stability exercises, and balancing exercises.
- Preventive measures for maintaining hip health include maintaining a healthy weight, warming up and cooling down, listening to your body, avoiding overuse, practicing good posture, and wearing appropriate footwear.
1. Understanding the Labrum and Hip Injuries
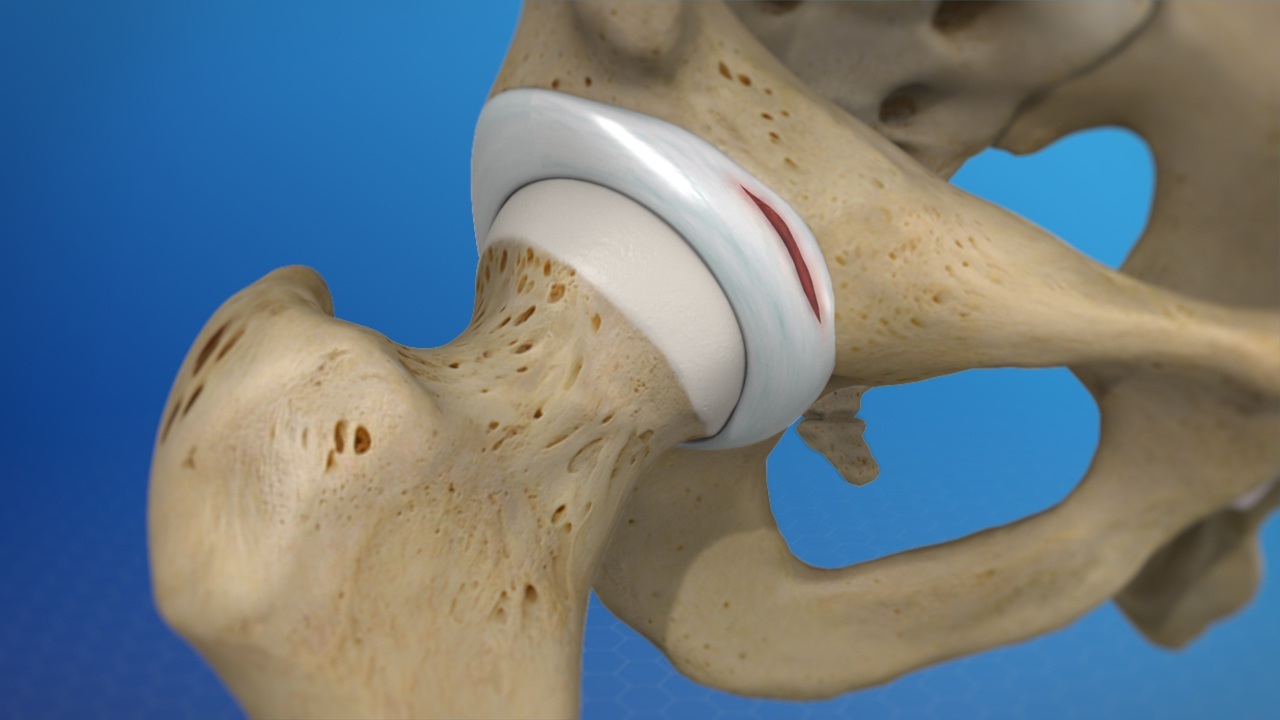
The labrum is a piece of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the hip joint. It provides stability and cushioning to the joint, allowing for smooth movement and preventing excessive friction between the bones. While the labrum is designed to withstand the forces and stresses placed on the hip, it can become torn due to various factors.
What is the labrum and how does it function?
The labrum is a fibrocartilaginous structure that extends from the outer rim of the acetabulum (the socket of the hip joint) to deepen it. It acts as a seal, providing stability to the joint and helping to hold the ball of the femur securely in place. The labrum also plays a crucial role in distributing the forces that are transmitted through the hip joint during movement and weight-bearing activities.
It functions as a shock absorber, reducing stress on the joint surfaces and protecting the articular cartilage from excessive wear and tear. The labrum also enhances joint lubrication, allowing for smooth movement and preventing bone-on-bone contact.
Common causes of a torn labrum in the hip
A torn labrum in the hip can result from various causes, including traumatic injuries, repetitive motions, and structural abnormalities. Some common causes include:
1. Trauma: A sudden impact or forceful injury, such as a fall or a direct blow to the hip, can lead to labral tears.
2. Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): FAI occurs when there is abnormal contact between the ball of the femur and the rim of the acetabulum. Over time, this can cause the labrum to tear.
3. Hip Dysplasia: In individuals with hip dysplasia, the hip socket is shallow, making the labrum more susceptible to tearing.
4. Repetitive Movements: Athletes or individuals who regularly participate in activities that involve repetitive hip motions, such as running or dancing, may develop labral tears due to overuse.
5. Degenerative Changes: As we age, the labrum can gradually deteriorate or become frayed, leading to tears.
2. Signs and Symptoms of a Torn Labrum
A torn labrum in the hip can cause a variety of signs and symptoms, which can vary depending on the severity and location of the tear. Some physical indications and typical symptoms of a torn labrum in the hip include:
Physical indications of a torn labrum
During a physical examination, a healthcare professional may observe certain signs that indicate a torn labrum, such as:
– Hip joint instability
– Limited range of motion
– Clicking or locking sensation in the hip
– Pain with specific movements or positions
Typical symptoms experienced by those with a torn labrum in the hip
Individuals with a torn labrum often experience several symptoms, including:
– Pain in the hip or groin area
– A deep, dull aching sensation
– Pain that worsens with weight-bearing activities, such as walking or standing
– Difficulty walking or running
– Stiffness and limited flexibility in the hip joint
– Clicking or popping sensations
It is important to note that not all individuals with a torn labrum will experience the same symptoms, and some may even be asymptomatic. Proper diagnosis by a medical professional is essential for determining the presence of a labral tear.
3. Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Medical tests and imaging techniques for diagnosing a torn labrum
If a torn labrum is suspected, a healthcare provider will typically perform a thorough physical examination and review the individual’s medical history. They may also recommend additional tests and imaging techniques to confirm the diagnosis, such as:
– Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI can provide detailed images of the hip joint and help identify the presence and location of a labral tear.
– X-rays: X-rays can help rule out other conditions and assess the overall structure of the hip joint.
– Hip Arthroscopy: In some cases, a minimally invasive procedure called hip arthroscopy may be performed to directly visualize the hip joint and confirm the presence of a labral tear.
Non-surgical treatment options for healing a torn labrum
Non-surgical treatment options are often the first line of treatment for a torn labrum in the hip. Some common non-surgical approaches include:
– Rest and activity modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate the symptoms and allowing the hip joint to rest can help alleviate pain and promote healing.
– Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a tailored exercise program to improve hip stability, strengthen the surrounding muscles, and enhance range of motion.
– Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
– Injection Therapy: In some cases, corticosteroid injections or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections may be recommended to provide temporary pain relief and facilitate the healing process.
Surgical intervention and post-operative care
If conservative measures fail to alleviate symptoms or in cases of severe labral tears, surgical intervention may be necessary. Hip arthroscopy is the most common surgical technique used to repair a torn labrum. During the procedure, small incisions are made, and specialized instruments are used to repair or remove the torn portion of the labrum.
Following surgery, a period of rehabilitation is crucial to optimize healing and restore full function to the hip joint. A physical therapist will guide the individual through a progressive rehabilitation program, including exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and joint stability. It is important to follow the post-operative care instructions provided by the surgeon to ensure a successful recovery.
4. Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery timeline for a torn labrum in the hip
The recovery timeline for a torn labrum in the hip can vary depending on the severity of the tear, the individual’s overall health, and adherence to rehabilitation protocols. In general, the recovery process can take several months. The following is a typical timeline:
– Phase 1 (0-6 weeks): This phase focuses on reducing pain and swelling, regaining range of motion, and restoring normal walking patterns.
– Phase 2 (6-12 weeks): During this phase, the emphasis shifts to strengthening the hip and surrounding muscles, improving balance and stability, and gradually returning to functional activities.
– Phase 3 (12 weeks and beyond): In the final phase, the focus is on advanced strengthening exercises, sport-specific training (if applicable), and gradual return to high-impact activities.
Exercises and stretches to aid in the healing process
A well-designed exercise program is crucial for the successful rehabilitation of a torn labrum in the hip. It is essential to work closely with a physical therapist or qualified healthcare professional to ensure exercises are performed correctly and gradually progressed. Some exercises and stretches that may be beneficial in the healing process include:
– Hip strengthening exercises: These may include hip bridges, clamshells, and side-lying leg lifts to target the muscles supporting the hip joint.
– Range of motion exercises: Gentle hip circles, leg swings, and seated hip stretches can help improve flexibility and restore normal joint motion.
– Core stability exercises: Strengthening the core muscles, such as the abdominals and lower back, can help improve overall stability and alleviate stress on the hip joint.
– Balancing exercises: Single-leg stance activities and balance board exercises can enhance proprioception and improve hip joint stability.
Preventing future labral tears and maintaining hip health
While not all labral tears can be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to reduce the risk of future injuries and maintain optimal hip health. Here are some tips:
– Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight places added stress on the hip joint, increasing the risk of labral tears. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce this risk.
– Warm up and cool down: Before engaging in physical activities, it is important to warm up with dynamic stretches and gradually increase intensity. Cooling down with gentle stretching afterward can help prevent muscle imbalances and excessive strain on the hip joint.
– Listen to your body: Pay attention to any pain or discomfort in the hip area. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention and address the issue promptly.
– Avoid overuse: Avoid repetitive activities or excessive training that places excessive strain on the hip joint. Incorporate rest days and cross-training activities to provide adequate recovery for the hip.
– Practice good posture: Maintaining proper posture during daily activities and exercise can help distribute forces evenly through the hip joint and reduce the risk of injury.
– Wear appropriate footwear: Choose footwear that provides adequate support and cushioning for the feet and hips, particularly during high-impact activities.
By following these preventive measures and incorporating healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can reduce their risk of labral tears and promote optimal hip health.
In conclusion, a torn labrum in the hip can be a painful and debilitating condition. However, with proper diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, individuals can heal and regain full function of their hip joint. Understanding the labrum, recognizing the signs and symptoms of a tear, and knowing the available treatment options are key to resolving the issue effectively. By following the provided guidelines and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can navigate the path to recovery and maintain long-term hip health.



